Ayahuasca: alkaloids, plants & analogs
Section 1 :
Structure & properties of Harmaline
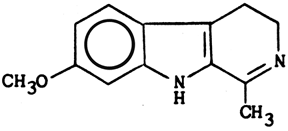
C13H14N2O
MW 214.27 CRC 61st
MW 214.3 Clarke's 1986
MW 214.26 Merck Index and Ott 1993
MW 214.266 Southon & Buckingham 1989
C 72.87%, H 6.59%, N 13.08%, O 7.47% Merck Index and Ott 1993
Free base:
mp 220-222° Chatterjee & Ganguly 1968
mp 227-229°. mmp with synthetic material (mp 228.5-231°) was not visibly depressed. Hochstein & Paradies 1957
mp 229-231° Orthorhombic bipyramidal prisms, tablets from methanol, rhombic octahedra from ethanol. Merck Index.
mp 236-238° Pale-yellow prisms after purification by sublimation.
Ghosal et al. 1971.
mp 238° Plates from dilute aqueous ammonia. Hasenfratz 1927
mp 239-240° (dec.) (Crystallized from absolute ethanol) Neuss 1964
mp 249-250° (dec.) Clarke 1986
mp 250° (dec.) Rhombic prisms from alcohol/ Tablets from methanol. CRC 1980-1981
mp 250-251° Telezhenetskaya 1977
mp 250-251° (227-229°)
Southon & Buckingham 1989
Vacuum distilled: bp 120-140° at 0.001 mm. Shulgin & Shulgin 1997
Sublimes in vacuum.
Hochstein & Paradies 1957
Sublimed at 110-120° (0.01 mm)
Ghosal et al. 1971
Insoluble in H2O.
Soluble in alcohol, benzene, chloroform and pyridine.
More water soluble than harmine. Precipitates after it in fractional crystallization.
Hasenfratz 1927
Said almost insoluble in pyridine Munir et al. 1995.
Munir implies that harmaline is more soluble in ethyl acetate than harmine and less soluble in chloroform than harmine.
Slightly soluble in water, alcohol, ether
Quite soluble in hot alcohol, dilute acids.
Merck Index
Soluble in Chloroform & in Alcohol.
Poethke et al. 1970
Slightly soluble in Water, Ethanol, Ether.
Clarke's 1986
K: 10-4.2 [Ed.: pK= log 1/k= 4.2]
Merck Index
Solutions fluoresce blue. Merck Index
Fluorescence spectrum: Bertrand 1945
Forms complex with mercury ions and precipitates. Base recovered after treating with hydrogen sulfide.
Harmaline-Mercury complex fluoresces blue and chromatographs lower than harmine-mercury complex.
Munir et al. 1995
UV:
UVmax (methanol): 218, 260, 376 nm (log ε 4.27, 3.90, 4.02) Merck 9th
uv spectrum (in methanol): ε218 = 18,760, ε260 = 7,980, ε376 = 10,460. Neuss 1964
UV λmax (DMSO/MeOH) 338.0 nm.
Munir et al. 1995
UVλmax (Ethanol) 231, 259 & 333 nm Chatterjee & Ganguly 1968
See also Cheng & Mitchelson 1997, Phillipson 1975 & Spenser 1959
IR:
Munir et al. 1995
Neuss 1964
Spenser 1959
Shulgin & Shulgin 1997
MS: Shulgin & Shulgin 1997
NMR: Munir et al. 1995
PMR: Robinson 1965
X-ray powder data: Neuss 1964
Detection using Fluorescence in Liquid chromatography: (Stationary phase: alkyl-modified silica gel/ Mobile phase Methanol-Water-Formic acid (166:34:1) adjusted to pH 8.5 with triethylamine)
Excitation: 396 nm
Emission: 475 nm
Popl et al. 1990
Chromatography of Harmaline:
Liquid: Eluted from alumina with Methanol.
Ghosal & Mazumdar 1971
tlc:
Solvent system Rf
Methyl alcohol-Chloroform-Acetic acid
(75:25:15) 0.38
Ghosal et al. 1971 [Silica Gel G chromatoplates]
Chloroform-Formamide 0.07
Hochstein & Paradies 1957
On Silica Gel (Dipped or sprayed with Potassium hydroxide [0.1M] and dried)
System Rf
Methanol-conc. Ammonium hydroxide
(100:1.5) 0.70
TLC reagent: Acidified Iodoplatinate
Clarke's Second 1986
tlc, glc: Phillipson 1975
Electrophoretic separation was reported by Cheng & Mitchelson 1997 using high-performance capillary electrophoresis (micellar electrokinetic chromatography)
Chromophores:
Reagent [Color]
Reagent formula.
Chloranil [Brown]
1% Chloranil in Acetonitrile.
CNTNF [Grey]
1% 9-Dicyanomethylene-2,4,7-trinitrofluorene in Acetonitrile.
Fluoranil [Yellow-brown turning Brown]
1% Fluoranil in Acetonitrile.
HNS [Yellow]
2,2',4,4',6,6'-Hexanitrobenzene in acetonitrile (Saturated).
TACOT [Yellow turning Orange turning Yellow-brown]
0.01% Tetranitro-2,3:5,6-dibenzo-1,3a,4,6a-tetra-azapentalene in Acetonitrile.
TetNF [Green]
1% 2,4,5,7-Tetranitro-9-fluorenone in Acetonitrile.
TCNE [Grey]
1% Tetracyanoethylene in Acetonitrile.
TNB [Brown turning Yellow-brown]
1% 1,3,5-Trinitrobenzene in Acetonitrile.
TNF [Yellow turning Green]
1% 2,4,7-Trinitro-9-fluorenone in Acetonitrile.
(All % as w/v). All freshly prepared before use.
Heacock & Forrest 1973
Tests on pure compound:
Mandelin's Test: Green-brown
Marquis test: Brown-green
Clarke's Second 1986
"Biofingerprint" in binding-reactivity assay of Terrapin Technologies (Terrrapin bioprofiling system):
Enzyme or receptor Approx. IC50
A1 Human glutathione-S-transferase 400-1000 mM
R8 rat glutathione-S-transferase >1000 mM
S1 schistosome glutathione-S-transferase >1000 mM
HF2 housefly glutathione-S-transferase >1000 mM
DAO porcine D-amino acid oxidase 40-400 mM
BCh equine butyryl cholinesterase < mM
Pap papain <4 mM
PDE snake venom phosphodiesterase I 400-1000 mM
This table is possibly erroneous as visible differentiation between 4-40 mM and <4 mM and between 40-400 mM and 400-1000 mM was inadequate in the b&w chart (fig. 8) of VanMiddlesworth & Cannell.
See p. 47 therein for more details on this assay or contact Terrapin Technologies.
Assay:
Usdin & Efron 1979 cited Der Marderosian et al. 1968 and Clarke 1969 [Also Clarke 1986]
See color reactions, tlc, UV & fluorescence above.
Isolations:
Göbel 1841 (The first isolation: from Peganum harmala seeds but mixed with harmine.)
Hochstein & Paradies 1957 (purported Banisteria caapi, used an unvouched pre-prepared extract)
Differentially extracted from an alkaline solution (pH 7.5-8.0 with NaOH) of harmine and harmaline by extracting harmine with chloroform and harmaline with ethyl acetate.
Also by treating a dried and purified mixture of the two with pyridine; in which Munir claims that harmaline is almost insoluble.
Munir et al. 1995
Synthesis:
Späth & Lederer 1930.
Spenser 1959.
Shulgin & Shulgin 1997 (from 6-MeO-tryptamine)
Structure:
Manske et al. 1927
Review of structure and synthesis work:
Merck Index cited Hofmann 1971
Coidentity with Harmidine: Robinson 1965
Harmaline hydrochloride:
Yellow, mp 212° Ott 1993
Hydrochloride dihydrate:
Slender yellow needles.
Moderately soluble in water and alcohol.
Merck Index
Soluble in water
Ott 1993
Insoluble in cold Sodium chloride solutions. Produced from the acetate (in solution) by the addition of sodium chloride.
Hasenfratz 1927
IR of harmaline hydrochloride dihydrate: Shulgin & Shulgin 1997
Harmaline acetate:
Needles mp 204-205°
Merck Index also Southon and Buckingham 1989
Water soluble. Readily converted to the hydrochloride by the action of sodium chloride.
Hasenfratz 1927
Hydriodide:
mp 232-235° (crystalline)
Chatterjee & Ganguly 1968


